
The following figure describes the major attributes of the Rhodonine family of chromophores:
RESONANT MOLECULES-- 2 OXYGEN'S
MEMBERS OF THE "INDICATOR" FAMILY
DERIVATIVES OF RETINOL
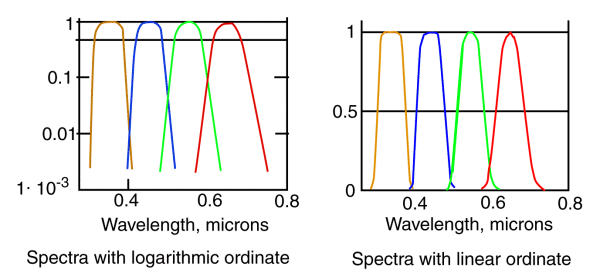
The SPECTRUMS OF THE RHODONINES [from Section 5.5.11]
All of the molecules have similar molecular weights. All exhibit a peak absorption in dilute solution near 493 nm. Only when in liquid crystalline state do they exhibit their biologically significant anisotropic spectrums.
The spectrums are shown using both logarithmic and linear ordinates. It is the logarithmic plot that is most relevant to vision.
The spectrums are shown normalized to the same peak value. Note how broad some of the individual peaks are. The specific shape is controlled by Fermi-Dirac Statistics. Only when measured with an inadequate spectrometer do they assume a more Gaussian shape (Actually, the shape of the individual spectrum approaches that of the spectraly selective filter in the spectrometer).
These spectrums peak at 625 nm for Rhodonine(5), 532 nm for Rhodonine (7), 437 nm for Rhodonine (9) and 342 nm for Rhodonine (11).
The bars under the molecules indicate the resonant length of each molecule on a relative scale. These lengths are proportional to the wavelengths of the resonant peaks of the molecules.
Return to the website home page